Introduction
Physiotherapy in Regina, Physiotherapy for Osteochondritis dissecans
Welcome to Alpha Center’s patient resource about adolescent osteochondritis dissecans of the elbow.
 Young gymnasts and overhand athletes, such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, swimmers, or volleyball players, are prone to a troubling elbow condition called osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). This condition occurs when blood flow to the elbow joint becomes restricted or is cut off, causing bone under the cartilage to slowly die. This issue originates from the forceful and repeated actions of sports, which strain the immature surface of the outer part of the elbow joint. The bone under the joint surface gradually weakens and becomes damaged. This compresses blood vessels that transport oxygen and nutrients to the bone. As a result of reduced blood flow, the small section of bone dies. The bone may also begin to crack, and fragments of the dead bone may break off and become lodged in different areas. OCD causes pain and reduced motion of the elbow.
Young gymnasts and overhand athletes, such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, swimmers, or volleyball players, are prone to a troubling elbow condition called osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). This condition occurs when blood flow to the elbow joint becomes restricted or is cut off, causing bone under the cartilage to slowly die. This issue originates from the forceful and repeated actions of sports, which strain the immature surface of the outer part of the elbow joint. The bone under the joint surface gradually weakens and becomes damaged. This compresses blood vessels that transport oxygen and nutrients to the bone. As a result of reduced blood flow, the small section of bone dies. The bone may also begin to crack, and fragments of the dead bone may break off and become lodged in different areas. OCD causes pain and reduced motion of the elbow.
In the past, this condition was called “Little Leaguer’s elbow”, because it was so common in baseball pitchers between the ages of 12 and 20. In more recent years, it has become increasingly apparent that additional sports, such as gymnastics and racket sports, subject the elbow to similar forces. Thus, these types of sports can also lead to OCD of the elbow in adolescent athletes.
This guide will help you understand:
- how this problem develops
- how doctors identify the problem
- what treatment options are available
#testimonialslist|kind:all|display:slider|orderby:type|filter_utags_names:Elbow Pain|limit:15|heading:Hear from some of our patients who we treated for *Elbow Pain*#
Anatomy
What part of the elbow does this problem affect?
The elbow is the connection of the upper arm bone (the humerus) and the two bones of the forearm (the ulna and the radius). The radius runs from the outer edge of the elbow down the forearm to the thumb side of the wrist.
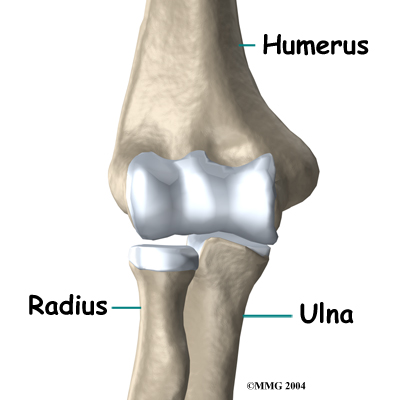
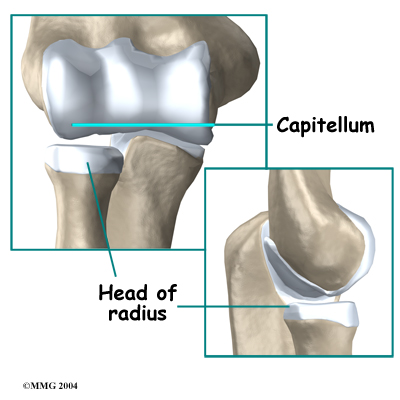
The joint where the humerus meets the radius is called the humeroradial joint. This joint comprises a bony knob and a shallow cup. The knob on the end of the humerus is called the capitellum. The capitellum fits into the cup-shaped end of the radius. This cup is called the head of the radius.
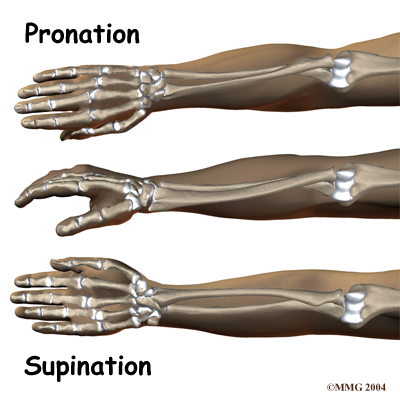
When the head of the radius spins on the capitellum, the forearm rotates to turn the palm up toward the ceiling (supination) or down toward the floor (pronation). The joint also hinges as the elbow bends and straightens.
In the elbow joint, the ends of the bones are covered by articular cartilage — a slick, smooth, fibrous material. Articular cartilage protects the bone ends from creating friction when they rub together as the elbow moves. The cartilage is also soft enough to act as a shock absorber. If articular cartilage is protected from injury, it is robust enough to last a lifetime.
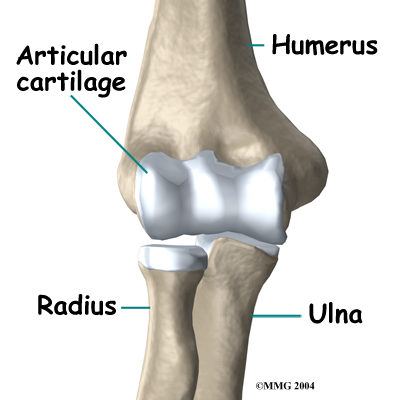
Elbow OCD affects the articular cartilage in the capitellum. It also impacts the layer of bone just below the cartilage, which is called the subchondral bone. In advanced stages of OCD, the upper end of the radius, particularly the head of the radius, is also affected.
Related Document: Alpha Center's Guide to Elbow Anatomy
Elbow Anatomy Introduction
Causes
How does this problem develop?
The cause of elbow OCD in adolescents is unknown. Scientists think that genetics is one possibility. This means that certain family members are more likely to develop OCD. The condition often occurs among relatives, and sometimes it is observed in several generations of the same family.
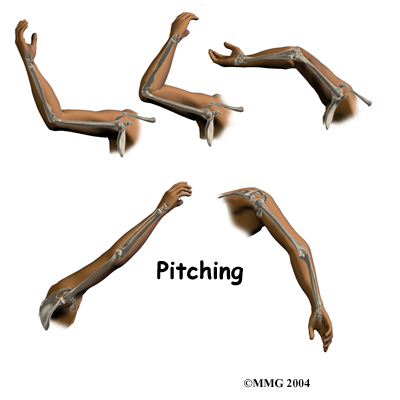
Another possible cause is that the blood supply to the humeroradial joint becomes blocked for reasons that are not clearly understood. Only the ends of a few small blood vessels enter the back of the humeroradial joint. If this scarce blood supply is damaged, there is no backup, meaning the body does not have a way to accommodate the loss of blood flow.
Although the exact cause of elbow OCD in adolescents is not known, most experts agree that overuse of the elbow plays a major role in its development.
For example, pitching can lead to an overuse strain and, in turn, cause elbow OCD. Throwing puts a lot of force on the elbow joint, and when this action is repeated frequently, it can damage the immature joint surface of an adolescent's elbow. After winding up and bending the arm back, the pitcher must quickly accelerate the arm to gain ball speed. However, the pitcher also has to almost immediately slow the arm down and follow through with the throw. In addition, the pitcher may angle the elbow outward slightly during the acceleration phase to get more ball speed. This action wedges the head of the radius against the capitellum. Furthermore, as the pitcher slows the arm down during the follow-through after a pitch, the forearm is fully pronated. This action puts extra pressure on the humeroradial joint.
Similarly, hitting a ball with a racket can strain the elbow in a similar manner as pitching a baseball. Gymnasts are also at risk of high forces on the capitellum when they repeatedly perform maneuvers with their hands and elbows locked out straight.
These actions done over and over again can eventually cause an overuse injury to the humeroradial joint of adolescent athletes. Adolescents' articular cartilage is newly formed and so can't handle these types of forces. The subchondral bone (under the articular cartilage) in the capitellum takes the brunt of the stress. A portion of the bone may eventually weaken, and possibly even crack. When the bone is damaged, the tiny blood supply going to the area is somehow blocked. Without blood supply, the small area of bone dies. This type of cell death is called avascular necrosis. ( Avascular means without blood, and necrosis means death.)
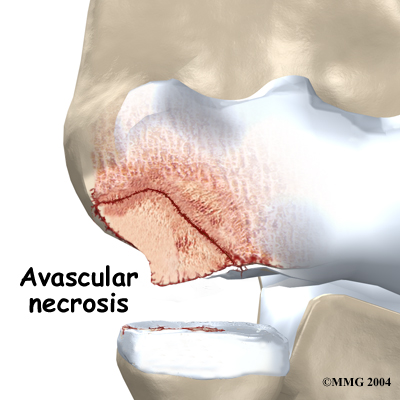
As the crack progresses, it may begin to separate. Eventually, the small piece of dead bone may break loose. This produces a separation between the articular cartilage and the subchondral bone, which is a condition called OCD. If the dead piece of bone completely detaches, it becomes a loose body that is free to float around the joint.
Another condition called Panner's disease also affects the capitellum in children. However, it is not the same as elbow OCD in adolescents. Panner's disease affects the bone growth center (the growth plate) of the capitellum. The disease impacts the entire capitellum, and usually heals completely when bone growth is complete. This condition generally occurs in kids (mainly boys) between the ages of 5 and 10.
Elbow OCD in adolescents is a different condition, in that it occurs after growth in the capitellum has stopped, which is usually between the ages of 12 and 15. Furthermore, OCD in adolescents only affects a portion of the capitellum, generally along the inside and lower edges of the bony knob. Unless elbow OCD is diagnosed and treated early, the prognosis is usually not as good as that of Panner's disease. In some cases, adolescents with elbow OCD develop elbow arthritis by early adulthood.
Symptoms
What does this problem feel like?
Only about 20 percent of adolescents with elbow OCD remember hurting their elbow. The remainder usually develop symptoms over time, which is typical with overuse injuries.
In the absence of a specific injury, an adolescent athlete may experience bothersome elbow discomfort at first, only while playing sports. The soreness generally goes away quickly when the elbow is rested. Over time, however, the elbow pain worsens, is hard to pinpoint, and may linger even when the arm is at rest. The elbow may also feel stiff, and it may not completely straighten.
In advanced cases of elbow OCD, the patient may notice that the joint grinds (called crepitus). The elbow may also catch or lock up occasionally. These sensations may mean that a loose body is floating around inside the elbow joint. The joint may also feel warm and swollen, and the muscles around the elbow may appear to have shrunk in size (atrophied).
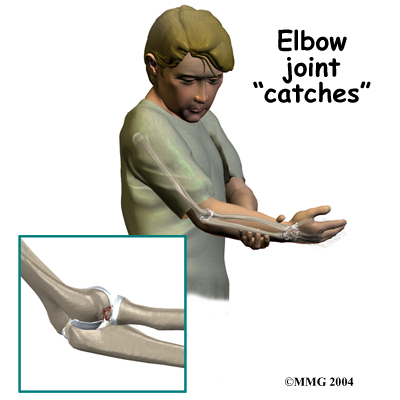
Moderate to severe cases of elbow OCD, and cases that are not caught and treated early, tend to create bigger problems later in life. Specifically, the joint may become arthritic early in adulthood. As a result, the patient may always have greater difficulty using the affected elbow.
Physician Diagnosis
How do doctors identify the problem?
The doctor begins by asking questions about the patient's age and participation in sports. During the physical exam, the sore elbow and healthy elbow will be compared. The doctor checks for tenderness by pressing on and around the elbow. The amount of movement in each elbow is measured. The doctor checks for pain and crepitus (grating) when the forearm is rotated and when the elbow is bent and straightened.
In addition, X-rays are needed to confirm the diagnosis. A front and side view of the elbow are generally the most helpful. In the early stages of OCD, X-rays may appear normal.
As the condition worsens, the X-ray image may show changes in the capitellum. The normal shape of the bony knob may appear irregular. In moderate to severe cases of elbow OCD, the capitellum might even look like it has flattened out, suggesting that the bone has collapsed. The X-ray may also show a crack in the capitellum, or even a loose body. In the late stages of elbow OCD, the radial head may appear enlarged, and the humeroradial joint might not be aligned as it normally should. These findings suggest early arthritis.
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may show more detail. The MRI can provide an impression of the size of the affected area. It can show bone irregularities and help detect swelling. Doctors may repeat the MRI scan at various times to see if the area is healing.
The doctor might also order a computed tomography (CT) scan. The CT scan helps confirm the diagnosis, as it clearly shows bone tissue. The doctor can compare CT scans over a period of time to monitor changes in the bones of the elbow.
Once you’ve been diagnosed with elbow OCD, you may need to discontinue your usual sport activities. This gives the elbow a chance to rest and helps promote healing. In addition, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medicine to help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Our Rehabilitation
At Alpha Center, our goal is to calm pain and inflammation by helping to protect the elbow from further harm. We might use ice, heat, or ultrasound to control inflammation, swelling, and pain. As symptoms ease, we will work with you to improve flexibility, strength, and muscle balance in the elbow.
Your elbow may also need to be rested. If your symptoms are especially severe, you may need to avoid activities that make the pain worse, including sports. Even after your symptoms ease up, activity may need to be restricted for another six to eight weeks.
When your elbow starts to feel better, we will give you exercises to help improve mobility. At first, your therapist will move your arm through passive therapy exercises. Later, the physiotherapists will guide you through active motion exercises, in which your muscles help do the work of moving the arm. As elbow motion and strength further improve, we will introduce more advanced strengthening exercises.
Our physiotherapists will also work with you to help improve your form in ways that reduce strain on your elbow during sports. Pitchers and racket-sport players might benefit from keeping the elbow aligned correctly, instead of angled outward, during the acceleration phase of the pitch or swing.
If your symptoms are especially severe, you may need to make changes that require less overhand activity. For example, pitchers could shift to playing first base. Gymnasts could also focus on maneuvers that don't stress the sore elbow. However, if the detached piece of bone is loose but still attached, all sports activities must be discontinued. Sports can begin again when you have no pain and show full elbow movement.
If your case is severe, you may also need to wear a sling or a long-arm splint for several weeks before starting elbow motion exercises. As symptoms ease and elbow movement improves, we will begin a guided program of strengthening and sport training.
When you are ready to resume sports activities, we will show you how to protect your injured elbow by applying ice. Ice treatments are simple to do: Place a wet towel on the elbow, then lay an ice pack or bag of ice over the elbow for 10 to 15 minutes. Ice treatments should be used after every sports activity.
Alpha Center provides services for physiotherapy in Regina, Physiotherapy.
What can you expect during rehabilitation?
If you require surgery for your OCD, your doctor may have you wait a few weeks before starting physiotherapy. During your first few physiotherapy treatments, our goal will be to control the pain and swelling following the surgery.
After you’ve recovered from surgery, we will guide you through exercises that help improve elbow motion, get your muscles toned, and restore your activity. First, we will exercise your elbow in positions and movements that don't strain the healing cartilage. As your program evolves, we will introduce more challenging exercises that safely advance the elbow's strength and function.
Most patients with elbow OCD will need to modify their activities after surgery. Most pitchers are unable to throw hard and struggle to completely avoid pain while throwing following the surgical procedure. In general, most athletes with elbow OCD need to stop playing high-level sports due to lingering elbow pain and reduced elbow motion.
If symptoms return, you will need to modify your activities until the symptoms subside. This includes avoiding high-intensity sports until you are no longer experiencing symptoms. Our physiotherapists can help you determine when it is safe to begin exercising your elbow again.
Alpha Center provides services for physiotherapy in Regina, Physiotherapy.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.


 Young gymnasts and overhand athletes, such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, swimmers, or volleyball players, are prone to a troubling elbow condition called osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). This condition occurs when blood flow to the elbow joint becomes restricted or is cut off, causing bone under the cartilage to slowly die. This issue originates from the forceful and repeated actions of sports, which strain the immature surface of the outer part of the elbow joint. The bone under the joint surface gradually weakens and becomes damaged. This compresses blood vessels that transport oxygen and nutrients to the bone. As a result of reduced blood flow, the small section of bone dies. The bone may also begin to crack, and fragments of the dead bone may break off and become lodged in different areas. OCD causes pain and reduced motion of the elbow.
Young gymnasts and overhand athletes, such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, swimmers, or volleyball players, are prone to a troubling elbow condition called osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). This condition occurs when blood flow to the elbow joint becomes restricted or is cut off, causing bone under the cartilage to slowly die. This issue originates from the forceful and repeated actions of sports, which strain the immature surface of the outer part of the elbow joint. The bone under the joint surface gradually weakens and becomes damaged. This compresses blood vessels that transport oxygen and nutrients to the bone. As a result of reduced blood flow, the small section of bone dies. The bone may also begin to crack, and fragments of the dead bone may break off and become lodged in different areas. OCD causes pain and reduced motion of the elbow.





